|
Caution: The current Shuttle website
is located here: http://www.shuttle.com
This website includes backup data for products until September 2004. |
| Products | Support | Glossary |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subchapters: Specification | Accessories | Mainboard FS51 | Download | Info/FAQ | Images | Press | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
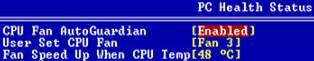
| 3 Phase Fan Speed | Fan Speed | Event |
| 1st Phased | 2200 RPM | Pre-selected Temp in Bios (72°C) |
| 2nd Phase | 3000 RPM | Pre-selected Temp in Bios (72°C) |
| 3rd Phase | 3300 RPM | Fail-safe Temp (80°C) |
Fail-safe Temp (80°C) When "CPU Fan AutoGuardian" feature is "Disabled", CPU fan will run at its default speed of approximately 3300 RPM.
We strongly recommend if you wish to use other brands fan cooler please disable "CPU Fan AutoGuardian" feature, allowing the CPU fan to run at its default speed. We only recommend for CPU Fan AutoGuardian feature enabled with enclosed fan cooler from Shuttle.
 TV/DVI add-on AGP card CV20
TV/DVI add-on AGP card CV20
What’s the maximum resolution for optional CV20 (TV-Out/DVI) add-on card to use in SS51G barebone?
SS51G barebone features SiS301MV chipset based TV-Out/DVI add-on card as an optional upgrade kit. The maximum input active resolution at PAL and NTSC system is 800x600. Because of the flexible scaling hardware, the over/under-scan (Active TV lines) modes supported by SiS301 are far beyond of these listed data below.
TV Output modes :
| System | Input (Active) resolution | Active TV Lines | Over/Under Scan |
| NTSC | 320x200 | 480 ~ 400 | + |
| 640x480 | 480 ~ 400 | + | |
| 720x480 | 480 ~ 400 | + | |
| 720x400 | 480 ~ 400 | + | |
| 800x600 | 480 ~ 420 | + | |
| PAL | 320x200 | 540 ~ 500 | + |
| 640x480 | 540 ~ 500 | + | |
| 720x400 | 540 ~ 500 | + | |
| 720x576 | 576 ~ 510 | + | |
| 800x600 | 600 ~ 510 | + |
LCD Output modes :
| Display Device | Input (Active) Resolution | Scaling |
| LCD 800x600 | 640x480 | Yes |
| 800x600 | No | |
| LCD 1024x768 | 640x480 | Yes |
| 800x600 | Yes | |
| 1024x768 | No | |
| LCD 1280x1024 | 640x480 | Yes |
| 800x600 | Yes | |
| 1024x768 | Yes | |
| 1280x1024 | No |
When using TV-Out function, the resolution shown on TV screen is either unclear or kind of fuzzy compared to that of fine resolution shown on regular CRT monitor. Why?
The observed output resolution lies in design and feature differences between TV and CRT monitor.
- In general, a 17" CRT monitor with 0.27mm dot pitch for crystal clear images, but TV only has horizontal line distance-to-distance.
- CRT monitor supports high resolution output & refresh rate. But on the other hand, TV only has low scan line.
- CRT monitor and TVs' Video's amplify specification is different.
What is the difference in Bios setting for Video Out between UTV and OTV?
SS51G has UTV and OTV function for use with optional upgradeable CV20 TV-Out/DVI add-on card, default is UTV/NTSC; it stands for underscan and overscan of TV-out. As you know, when enabling TV Out, the picture will not always fill the TV screen. The reason for that is that we use "underscan" if TV Out is enabled in order to make sure that all buttons, especially the ones in the corners of the screen, are fully visible. But the image out is not in full screen mode on TV. UTV is ideal for PC based environment.
There is a bios switch which enables an "overscan" mode for TV Out. This overscan mode results in absolutely no visible border on the TV. The picture coming from the PC will be larger than the picture displayed on TV. OTV is ideal for pure TV-out environment such as Karaoke entertainment or road show demonstrations.
There are some IMPORTANT points you should note:
- Some buttons (close, minimize etc.) may not be accessible if the application is in full screen mode (OTV), they are outside the visible range of the picture.
- Your PC Monitor will most likely switch OFF, because it can not support overscan (some monitor may be switched off automatically)
- The TV Out picture can NOT be adjusted, you can not use overscan and then downsize the picture so that it exactly fits the screen.
 What is SPDIF?
What is SPDIF?
SPDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) is a standard audio transfer file format. It’s usually found on digital audio equipment such as a DAT machine or audio processing device. SS51G barebone features SPDIF In/Out function. SPDIF interface allows the transfer of audio from one file to another without the conversion to and from an analog format, which could degrade the signal quality.
 How to install PCI VGA card in SS51G?
How to install PCI VGA card in SS51G?
Please follow these procedures to install PCI VGA card:
- Boot up to Windows without PCI video card installed. Disable SiS651 display adapters in Device Manager under Windows.
- Reboot and change "Init Display First" to [PCI Slot] under Integrated Peripherals in CMOS Setup Utility in Bios, then save & exit.
- Shut down system and install PCI VGA card. Boot up into Windows by using PCI video card as primary display device.
- Install PCI video card drivers, and reboot the system.
- Enter CMOS Setup Utility during POST while rebooting, disable Onboard VGA in Bios, then save & exit.
 Hardware Monitoring Tools
Hardware Monitoring Tools
What temperature monitoring utilities are available? A7The following links contain freeware/shareware for CPU/System/HDD temperature monitoring utilities :
- Motherboard Monitor (MBM) http://mbm.livewiredev.com/
- Hardware Sensors Monitor http://www.hmonitor.com/
- SpeedFan http://www.almico.com/speedfan.php
- SiSoftware Sandra http://www.sisoftware.demon.co.uk/
- HDD Temperature http://www.hddtemp.com/
- Drive Temperature http://private.peterlink.ru/tochinov/
- System Monitoring http://winpulse.com/
 Why my copper heat-pipe has a silver finish look?
Why my copper heat-pipe has a silver finish look?
Production heat-pipe is coated with nickel metal. The nickel coating enhances the heat-pipe structure and effectively prevents copper heat-pipe from environmental surface corrosion and tarnishing. It is the nickel coating which gives the heat-pipe the silver finish look, it is not made of aluminum, nor a cost down version made of aluminum material. It is copper heat-pipe anodized with Nickel. The structural integrity and heat transfer efficiency of the copper heat-pipe is unchanged. For production heat-pipe, Shuttle made it not only look more elegant, but also structural enhanced and copper corrosion resistant.
 How does Shuttle I.C.E. heat pipe technology work?
How does Shuttle I.C.E. heat pipe technology work?
A heat pipe is a heat transfer device with an extremely high effective thermal conductivity. Heat pipe is a vacuum tight vessel which is evacuated and partially back-filled with a working fluid. Heat pipes transfer heat by the evaporation and condensation of a working fluid. As heat is input at the evaporator, fluid is vaporized, creating a pressure gradient in the pipe. This pressure gradient forces the vapor to flow along the pipe to the cooler section where it condenses, giving up its latent heat of vaporization. The working fluid is then returned to the evaporator by capillary forces developed in the porous wick structure or by gravity.
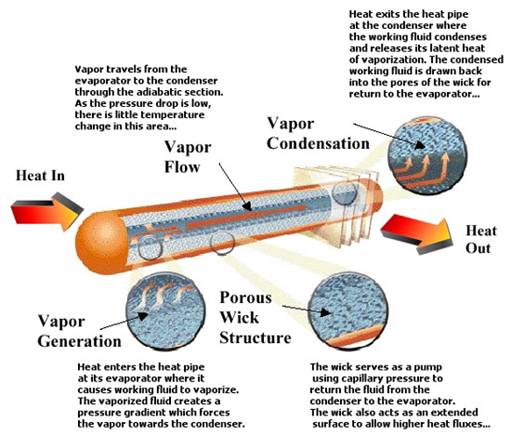
Heat pipes do not have a set thermal conductivity like solid materials due to the two-phase heat transfer. Instead, the effective thermal conductivity improves with length. Unlike solid materials, a heat pipe's effective thermal conductivity will also change with the amount of power being transferred and with the evaporator and condenser sizes. For a well designed heat pipe, effective thermal conductivity can range from 10 to 10,000 times the effective thermal conductivity of copper depending on the length of the heat pipe.
How does Shuttle I.C.E. heat pipe technology overcome the noise and heat concerns commonly faced with P4 fan heatsink coolers?
Shuttle I.C.E. heat pipe is equipped with aluminum heatsink with copper base to quickly adsorbed and effectively transfer the heat generated from the CPU through the special designed copper heat pipe up to the thin fins, where the heat is then being cooled down by 8cm, low RPM noise-reduced fan.
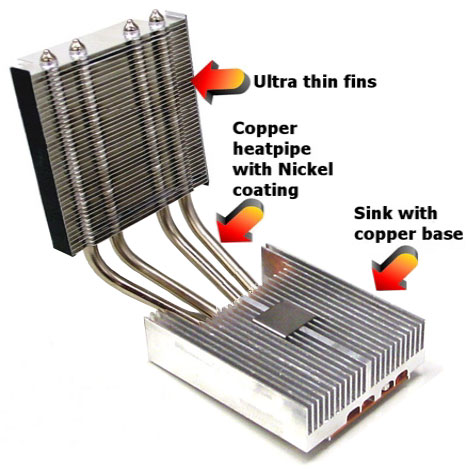
This 8cm, low RPM noise-reduced fan blows the hot air out of the system through the back panel, leaving the entire system not only cool, but very quiet when compared to other noisy Socket A fan heatsink coolers on the market.

Use in conjunction with CPU Fan AutoGuardian feature (default enabled) in Bios. The cooler fan can stay at an ultra quiet mode of about 2200 RPM, and yet still outperforms other noisy tornado-like fan heatsink coolers.
| Navigation |
Shuttle Computer - European Headquarters +++ Disclaimer +++ Last update: 30.4.2008