|
Achtung: Die aktuelle
Shuttle-Website finden sie unter http://www.shuttle.com
! Diese Website enthält Archivdaten, deren Aktualität nicht gewährleistet werden kann. |
| Produkte | Support | Index |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unterkapitel: Spezifikation | Info/FAQ | Download | Presse | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Designed for Windows XP Logo |
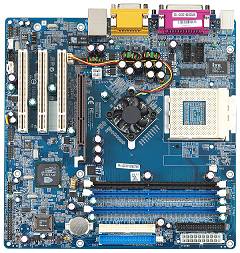
 CPU-Unterstützung MN31/N
CPU-Unterstützung MN31/N
| FSB | Multiplikator | Prozessor |
|---|---|---|
| 100MHz | 13x | AMD Duron(Morgan) 1.30 GHz |
| 100MHz | 12x | AMD Duron(Morgan) 1.20 GHz |
| 100MHz | 11x | AMD Duron(Morgan) 1.10 GHz |
| 100MHz | 10x | AMD Duron(Morgan) 1.00 GHz |
| 100MHz | 9.5x | AMD Duron 950 MHz |
| 100MHz | 9x | AMD Duron 900 MHz |
| 100MHz | 8.5x | AMD Duron 850 MHz |
| 100MHz | 8x | AMD Duron 800 MHz |
| 100MHz | 7.5x | AMD Duron 750 MHz |
| 100MHz | 7x | AMD Duron 700 MHz |
| 100MHz | 6.5x | AMD Duron 650 MHz |
| 100MHz | 6x | AMD Duron 600 MHz |
| 100MHz | 13x | AMD Duron (Palomino) 1.30 GHz |
| 133MHz | 13.5x | AMD Duron (Applebred) 1.80 GHz |
| 133MHz | 12x | AMD Duron (Applebred) 1.60 GHz |
| 133MHz | 10.5x | AMD Duron (Applebred) 1.40 GHz |
| 166MHz | 13.5 x | AMD Athlon XP 2800+ |
| 166MHz | 13x | AMD Athlon XP 2700+ |
| 166MHz | 12.5x | AMD Athlon XP 2600+ |
| 133MHz | 16x | AMD Athlon XP 2600+ |
| 166MHz | 12 x | AMD Athlon XP 2500+ |
| 166MHz | 11.5 x | AMD Athlon XP 2400+ |
| 133MHz | 15x | AMD Athlon XP 2400+ |
| 133MHz | 13.5x | AMD Athlon XP 2200+ |
| 133MHz | 13x | AMD Athlon XP 2100+ |
| 133MHz | 12.5x | AMD Athlon XP 2000+ |
| 133MHz | 12x | AMD Athlon XP 1900+ |
| 133MHz | 11.5x | AMD Athlon XP 1800+ |
| 133MHz | 11x | AMD Athlon XP 1700+ |
| 133MHz | 10.5x | AMD Athlon XP 1600+ |
| 133MHz | 10x | AMD Athlon XP 1500+ |
| 133MHz | 15x | AMD Athlon XP (Thorton) 2400+ |
| 133MHz | 13.5x | AMD Athlon XP (Thorton) 2200+ |
| 133MHz | 12.5x | AMD Athlon XP (Thorton) 2000+ |
| 166MHz | 13x | AMD Athlon XP (Barton) 3000+ |
| 166MHz | 12.5x | AMD Athlon XP (Barton) 2800+ |
| 166MHz | 11.5x | AMD Athlon XP (Barton) 2600+ |
| 166MHz | 11x | AMD Athlon XP (Barton) 2500+ |
| 100MHz | 9.5x | AMD Athlon 950 MHz |
| 100MHz | 9x | AMD Athlon 900 MHz |
| 100MHz | 8.5x | AMD Athlon 850 MHz |
| 100MHz | 8x | AMD Athlon 800 MHz |
| 100MHz | 7.5x | AMD Athlon 750 MHz |
| 100MHz | 7x | AMD Athlon 700 MHz |
| 100MHz | 6.5x | AMD Athlon 650 MHz |
| 133MHz | 10.5x | AMD Athlon 1.40 GHz |
| 100MHz | 14x | AMD Athlon 1.40 GHz |
| 133MHz | 10x | AMD Athlon 1.33 GHz |
| 100MHz | 13x | AMD Athlon 1.30 GHz |
| 133MHz | 9x | AMD Athlon 1.20 GHz |
| 100MHz | 12x | AMD Athlon 1.20 GHz |
| 133MHz | 8.5x | AMD Athlon 1.13 GHz |
| 100MHz | 11x | AMD Athlon 1.10GHz |
| 133MHz | 7.5x | AMD Athlon 1.00 GHz |
| 100MHz | 10x | AMD Athlon 1.00 GHz |
| Bemerkung: | ||
 Unterschiede zwischen dem ersten und zweiten nForce-Chipsatz
Unterschiede zwischen dem ersten und zweiten nForce-Chipsatz
| Chipsatz | nForce (Sept. 2001) | nForce2 (Juli 2002) |
| Chipsatz | nForce 430 / 430-T nForce 420 / 420-T nForce 415 / 415-D nForce 230 / 230-T nForce 220 / 220-D | nForce2 GT = IGP + MCP-T nForce2 G = IGP + MCP2 nForce2 ST = SPP + MCP-T nForce2 S = SPP + MCP2 |
| CPU | AMD Duron, Athlon XP (S462) 100 und 133MHz FSB | AMD Duron, Athlon XP (S462) 100, 133 und 166MHz FSB |
| Speicher | DDR200, DDR266 max. 3072MB, max 3 DIMMs asynchroner Modus möglich Bei 2xx 64-Bit, sonst 128-Bit | DDR200, 266, 333, 400 max. 3072MB, max 3 DIMMs asynchroner Modus möglich 128-Bit TwinBank Architecture |
| IDE | UltraDMA/33/66/100 (bei 230/T, 430/T: ATA133) | UltraDMA/33/66/100/133 |
| Integrierte Grafik | GeForce2 MX (nicht bei 415x) | GeForce4 MX Dual VGA (nur bei IGP-Version) |
| AGP | 4x Modus | 4x, 8x Modus |
| PCI | max 6 | max 6 |
| USB | 6x USB 1.1 (bei 230/T, 430/T: USB2.0) | 6x USB 2.0 |
| Firewire 1394 | nur bei 230-T und 430-T | nur bei MCP-T |
| Sound (APU) | Dolby Digital 5.1 bei D/T-Typ, sonst AC'97 | Dolby Digital 5.1 nur bei MCP-T, sonst AC'97 |
Erklärungen zu den Abkürzungen:
Northbridge
SPP (System Plattform Processor) = Northbridge ohne Grafik
IGP (Integrated graphics processor) = Northbridge mit Grafik
IGP-64 mit einem Speicherkanal
IGP-128 mit zweikanal-Speicher-Interface
Southbridge
MCP (Media und Communications Prozessor) = Southbridge mit NVidia ethernet
MCP-T (zusätzlich: zusätzlich 3COM ethernet, Firewire, APU)
APU (Audio Processing Unit mit DolbyDigital 5.1 Encoder)
HyperTransport: Verbindung zwischen North- und Southbridge max. 800 MB/s
 Download MN31N
Download MN31N
Download-Dateien:
- Bitte prüfen Sie diesen Link für neueste Download-Dateien
- Winflash Utility - binäre BIOS Updates under Windows (1 MB)
- BIOS Info: EXE-Datei nicht unter Windows/DOS-Box starten!
- Bios-Update MN31S00I (Mainboard MN31N) als BIN-Datei
- Bios-Update MN31S00I (Mainboard MN31N) als ZIP-Datei
- BIOS Info (Mainboard MN31/N)
- USB Treiber für MN31/N/L (410 kB)
- USB Patch für MN31/N (328 kB)
- Englisches Handbuch MN31/N (PDF, 8.2 MB)
- Download the FREE Acrobat Reader Software
| Navigation |
Shuttle Computer Deutschland +++ Disclaimer +++ Letztes Update: 30.4.2008