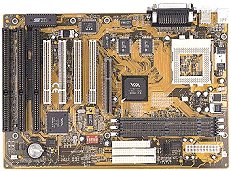
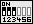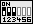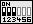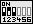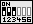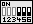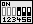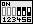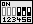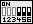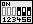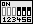Pfad: Home Mainboard HOT-595
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Einstellungen zum Prozessor | |||||
| Prozessor | CPU- | System- | Multi- | Vcore | Vio |
| Intel Pentium P55C MMX | 233 MHz | 66 MHz | 3,5 x | 2,8V | 3,3V |
| Intel Pentium P55C MMX | 200 MHz | 66 MHz | 3 x | 2,8V | 3,3V |
| Intel Pentium P55C MMX | 166 MHz | 66 MHz | 2,5 x | 2,8V | 3,3V |
| Intel Pentium P54C | 200 MHz | 66 MHz | 3 x | 3,3V | 3,3V |
| Intel Pentium P54C | 166 MHz | 66 MHz | 2,5 x | 3,3V | 3,3V |
| Intel Pentium P54C | 150 MHz | 60 MHz | 2,5 x | 3,3V | 3,3V |
| Intel Pentium P54C | 133 MHz | 66 MHz | 2 x | 3,3V | 3,3V |
| Intel Pentium P54C | 120 MHz | 60 MHz | 2 x | 3,3V | 3,3V |
| Intel Pentium P54C | 100 MHz | 66 MHz | 1,5 x | 3,3V | 3,3V |
| Intel Pentium P54C | 90 MHz | 60 MHz | 1,5 x | 3,3V | 3,3V |
| Intel Pentium P54C | 75 MHz | 50 MHz | 1,5 x | 3,3V | 3,3V |
| AMD K6-2 | 333 MHz | 66 MHz | 5 x | 2,2V | 3,3V |
| AMD K6-2 | 300 MHz | 66 MHz | 4,5 x | 2,2V | 3,3V |
| AMD K6-2 | 266 MHz | 66 MHz | 4 x | 2,2V | 3,3V |
| AMD K6 | 266 MHz | 66 MHz | 4 x | 2,2V | 3,3V |
| AMD K6 | 233 MHz | 66 MHz | 3,5 x | 3,2V | 3,3V |
| AMD K6 | 200 MHz | 66 MHz | 3 x | 2,9V | 3,3V |
| AMD K6 | 166 MHz | 66 MHz | 2,5 x | 2,9V | 3,3V |
| AMD-K5 | PR166 | 66 MHz | 2,5 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| AMD-K5 | PR133 | 66 MHz | 2 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| AMD-K5 | PR120 | 60 MHz | 2 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| AMD-K5 | PR100 | 66 MHz | 1,5 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| AMD-K5 | PR90 | 60 MHz | 1,5 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| AMD-K5 | PR75 | 50 MHz | 1,5 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| Cyrix/IBM 6x86MX **) | PR266 | 66 MHz | 3,5 x | 2,9V | 3,3V |
| Cyrix/IBM 6x86MX **) | PR233 | 75 MHz *) | 2,5 x | 2,9V | 3,3V |
| Cyrix/IBM 6x86MX **) | PR200 | 75 MHz *) | 2 x | 2,9V | 3,3V |
| Cyrix/IBM 6x86MX **) | PR166 | 60 MHz | 2,5 x | 2,9V | 3,3V |
| Cyrix/IBM 6x86L | P200+ | 75 MHz *) | 2 x | 2,8V | 3,3V |
| Cyrix/IBM 6x86L | P166+ | 66 MHz | 2 x | 2,8V | 3,3V |
| Cyrix/IBM 6x86L | P150+ | 60 MHz | 2 x | 2,8V | 3,3V |
| Cyrix/IBM 6x86 | P200+ | 75 MHz *) | 2 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| Cyrix/IBM 6x86 | P166+ | 66 MHz | 2 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| Cyrix/IBM 6x86 | P150+ | 60 MHz | 2 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| Cyrix/IBM 6x86 | P133+ | 55 MHz | 2 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| Cyrix/IBM 6x86 | P120+ | 50 MHz | 2 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| IDT-C6 | 200 MHz | 66 MHz | 3 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| IDT-C6 | 180 MHz | 60 MHz | 3 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
| IDT-C6 | 150 MHz | 60 MHz | 2,5 x | 3,52V | 3,52V |
*) Mit 75 MHz Systemtakt werden Chipsatz und PCI-Bus übertaktet. Da der Takt-Multiplikator einer Cyrix/IBM 6x86(L) P200+ CPU auf 2 festgelegt ist, ist eine Systemtakt-Einstellung von 75 MHz in diesem Fall unumgänglich, wenn die Leistungsfähigkeit dieser CPU ausgereizt werden soll.
**) Bei Cyrix/IBM 6x86MX ist die auf der CPU aufgedruckte Takt-Einstellung zu wählen.
Automatische CPU-Spannungserkennung
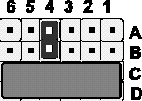
| Die Spannung wird automatisch eingestellt, wenn der Jumper-Block auf der Reihe B-C des Jumpers SW1 entsprechend der Abbildung (rechts) gesetzt ist. | SW1 |
In der Tabelle oben sind die CPU-Spannungen angegeben, die bei automatischer Erkennung eingestellt werden. Falls die verwendete CPU eine andere Spannung benötigt, ist diese manuell einzustellen, zum Beispiel bei:
- Intel Pentium P54C (ohne MMX): der VRE-Typ hat einen Spannungsbereich von 3,4 bis 3,6V. Einzustellen sind dann 3,52V
- AMD K6 CPU mit 233 MHz ist auch mit Vcore=3,3V erhältlich.
-
Cyrix/IBM 6x86 ist auch als 3,3V-Typ erhältlich.
Manuelle CPU-Spannungseinstellung per Jumper
| Zur manuellen Einstellung der CPU-Spannung muß der Jumper-Block von SW1 auf Position C-D gesetzt werden. Zusätzlich werden auf den Reihen A-B entsprechend der folgenden Tabelle einzelne Jumper gesetzt. Rechts: Beispiel für Vcore=2,8V (Vio=3,3V) | SW1 |
| Manuelle CPU-Spannungseinstellung | |
| CPU-Spannung | JP33 |
| 3,52V |
|
| 3,4V |
|
| 3,3V |
|
| 3,2V |
|
| 3,1V |
|
| 3,0V |
|
| 2,9V |
|
| 2,8V |
|
| 2,7V |
|
| 2,6V |
|
| 2,5V |
|
| 2,4V |
|
| 2,3V |
|
| 2,2V |
|
| 2,1V |
|
| 2,0V |
|
Falls Vcore und Vio gleich sind, handelt es sich um eine Single-Voltage-CPU mit einfacher Spannungsversorgung (im Gegensatz zur Dual-Voltage CPU). Hierfür sind die Spannungseinstellungen 3,3V, 3,4V und 3,52V
Systemtakt
Der Systemtakt wird mit Schalter 1 bis 3 des DIP-Miniturschalters SW2 eingestellt.
Beispiel für "66 MHz" Systemtakt: Schalter 1 bis 3 auf Stellung "off".
| Takt-Einstellung für System und PCI-Bus | ||
| Systemtakt | PCI-Bus-Takt | SW2 |
| 50 MHz | 25 MHz |
|
| 60 MHz | 30 MHz |
|
| 66 MHz | 33 MHz |
|
| 75 MHz *) | 37,5 MHz |
|
| 83 MHz *) | 41,5 MHz |
|
*) Bemerkung: Mit den Systemtakt-Einstellungen 75 MHz und 83 MHz wird der Chipsatz übertaktet. Die empfohlene Einstellung ist 66 MHz.
Multiplikator
Das Verhältnis zwischen internem CPU-Takt und dem Systemtakt des Mainboards wird kurz Multiplikator bezeichnet. Er wird mit Schalter 4 bis 6 des DIP-Miniturschalters SW2 eingestellt.
Beispiel für Multiplikator "1,5": Schalter 4 bis 6 auf Stellung "off".
| Takt-Multiplikator | |
| Multiplikator | SW2 |
| 1,5 x |
|
| 2 x |
|
| 2,5 x |
|
| 3 x |
|
| 3,5 x |
|
| 4 x |
|
| 4,5 x |
|
| 5 x |
|
| 5,5 x |
|
| 6 x |
|
Sonstige Einstellungen
| CMOS-Speicher löschen - JP6 | |
| normale Position |
|
| CMOS löschen (Rechner dabei ausgeschalten) |
|
| Flash EPROM Programmierspannung - JP13 | |
| 12V (Intel, MXIC) |
|
| 5V (SST, Atmel, Winbond) |
|
| Reservierter Jumper - JP1 und JP3 | |
| JP1 |
|
| JP3 |
|
![]()
Druck-Version der Originalseite: http://de.shuttle.com/595_conf.htm
Shuttle Computer Deutschland - Änderungen und Druckfehler vorbehalten. Datum:
30.4.2008